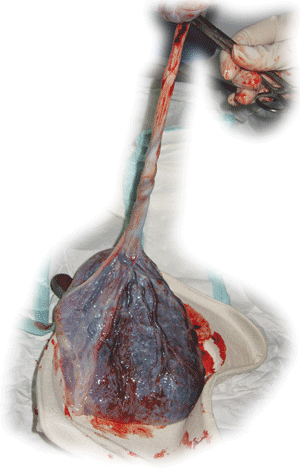
The term "cord blood" is used for blood that is drawn from the umbilical cord and the placenta after a baby is born. Until recently this afterbirth was discarded as biological waste. Cord blood contains stem cells that may be frozen for later use in medical therapies, such as cord blood transplants or clinical trials of new cell therapies, tissue engineered organs, isolating growth factors, etc. These are different from both the embryonic stem cells in a fertilized egg and any stem cells obtained from a child or an adult person. The stem cells in cord blood can grow into blood and immune system cells, as well as other types of cells.
Baby gets nourishment in mother's womb through umbilical cord. The placenta forms the anchor and a barrier to many molecules trying to enter into the baby's body through the cord while umbilical cord forms the channel for transport of nutrition to the baby. Once the child is delivered, this important channel becomes useless and is generally thrown away as a biological waste. The umbilical cord and placenta are rich sources of stem cells. Researchers have been able to isolate stem cells from the umbilical cord and placenta as well. The stem cells so obtained are pluripotent of both mesenchymal and hematopoietic lineage, that is these cells are capable of differentiating into not only blood cells but also can give rise to cells of heart, lungs, bones, muscles, etc.
Collection
Once a couple decides to preserve their child's cord blood they sign an agreement with the company. After which a collection kit is provided to the couple with details about the collection process of cord blood. This kit is handed over to the obstetrician at the time of delivery. After delivery of the baby, cord blood is collected using sterile blood bag needle. The collection procedure is totally harmless to the mother and child. The bag and the tubes are then packed in a box of icepacks, company personnel collects the kit and transfers it to the laboratory.
Processing
The sample is processed in the lab using a unique technology developed at Stem Plus where minimum reagents are used to isolate not only stem cells but also VSELS cells which are much more potent than stem cells.
Banking
Stem cells isolated from cord blood are stored at -196°C in liquid nitrogen. These cells can be preserved for years without deterioration and can be used as and when required. Since, nitrogen is at -196°C in liquid phase, preservation is not dependent on electricity supply for cooling purpose and thus, deterioration due to power failure does not take place.






